This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Algorithms and Flowchart
The algorithm is a step-by-step instruction, guideline or rule to performe some action or reach the solution for given problem. Flowchart is one of the way to represent algorithm graphically, where graphical elements like boxes, squares, circles, and arrows connecting them represent flow of control. Every element can represent on step in the instructions.
Simplified flowchart elements:
Start
End
Action or expression
Rectangle. Inside rectangle a name of the action, name of the sub-routine or short decsiption can be written. Similar actions can be included into one general action.
Sequence
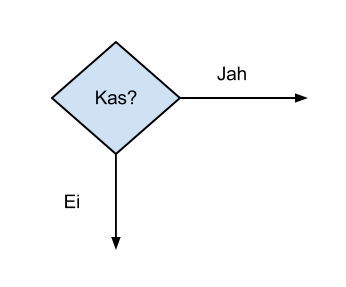
Condition / Decision
Diamond (rhombus). Inside diamond is a logical expression and in most cases two arrows are drawn out from diamond. One is when logical expression results True (Yes/1) and other when expression result is False (No/0). Always bot arrows have to be labeled. In special case only one arrow can be used as output from diamond. The case is when logical expression can clearly result only one solution, e.g. True. This is the case where for example endless cycle is used in program code (e.g. while (true)).
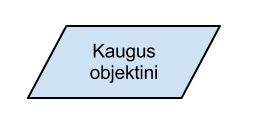
Data exchange
Trapezoid. Inside trapetzoid a name or activity is described. In robotics it is usually used to communicate with sensors and user. For simplification also normal rectangle action can be used instead of trapezoid.
Examples
Voodiagrammide koostamiseks võib kasutada tavalist kontoritarkvara nn MS Word või MS Excel, OpenOffice/LibreOffice Writer või Calc, kuid mugavam on kasutada spetsiifilisi programme nn MS Visio või OpenOffice/LibreOffice Draw
Mikrokontrollerite tarkvara algoritmide voodiagrammidel üldjuhul programmi lõppu ei ole ja kogu tegevus on ühes lõputus tsüklis. Lõputu tsükli väljumistingimus ei saa kunagi tõeseks ja sellepärast on lubatud selle tähistamine rombiga, millel on ainult üks väljund. tingimus ise on märgitud lihtsalt true või 1. Diagrammide koostamisel tuleks jälgida, et kui programmis on hargnemised, siis saab see olla ainult läbi rombi (tingimuslause). Koondumised võivad olla ka mujal.
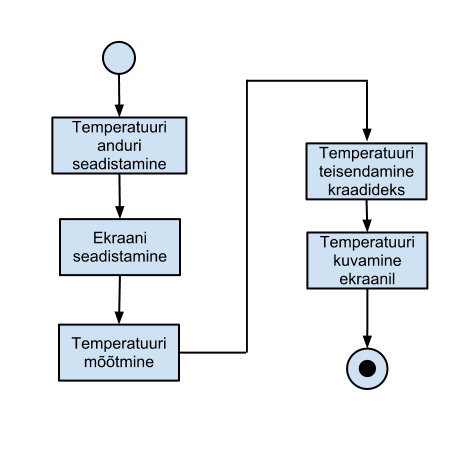
Järgnevad näited illustreerivad plokkide kasutamist algoritmi juures. Esimene näide on lihtne ilma tsüklite ja sisendite kontrollita algoritm ühekordse tegevuse teostamiseks.
Järgnev diagramm kirjeldab süsteemi, mis kontrollib 1 m ala ja kui kontrollitavasse alasse siseneb objekt, käivitab kümneks sekundiks alarmi. alarm töötab niikaua, kui objekt on kontrollitavast alast väljunud.