This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Indoor Mobile Robot
TurtleBot is a flexible robotic platform designed to work with ROS. Built from common components, TurtleBot is modular and therefore allows the user to create many different configurations. Turtlebot is the ideal platform for experimenting with and learning about ROS. There are many users of the turntable, which means that many functions are freely available on the Internet in the form of ROS nodes. You don't have to write any lines of code to get Turtlebot to automatically navigate the space. All you need to do is find the right nodes on the Internet and get them working.

Most recent and developed version of the turtlebot is version 3. TurtleBot3 is made up of modular plates that users can customize the shape. Available in three types: small size Burger and medium-size Waffle, Waffle Pi. TurtleBot3 consists of a base, two Dynamixel motors, a 1,800mAh battery pack, a 360 degree LIDAR, a camera(+ RealSense camera for Waffle kit, + Raspberry Pi Camera for Waffle Pi kit), an SBC(single board computer: Raspberry PI 3 and Intel Joule 570x) and a hardware mounting kit attaching everything together and adding future sensors. Turtlebot3 was released in May 2017.
Sensors
The main sensor of the turtlebot is the 360 Laser Distance Sensor LDS-01. The LDS-01 is a 2D laser scanner capable of sensing 360 degrees that collects a set of data around the robot to use for SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping). The below fidure shows that how a the robot sees the environment from a 360 laser sensor. The blue laser rays are reflected from the objects and the distance is measured and finally a 2D point-cloud of the environment is built.
The 3D camera is one of the most versatile robot sensors. One output of a 3D camera is a 2D camera image, which means that various object recognition algorithms can be used. Many machine vision libraries are available for ROS. One of the most widely used and versatile is OpenCV. In addition, for example, the most up-to-date artificial intelligence library You only look once (YOLO) is available. The same library is used by Iseauto for object recognition.
Objects will be identified and a box will be drawn around them, with the name of the object type identified:
The advantage of a 3D camera over a conventional camera is the depth dimension. This allows the robot to sense the distance between objects. This feature allows the robot to develop autonomous navigation.
Turtlebot 3 Simulation
To simulate a turtle robot, everything you need to simulate a Gazebos robot is freely available on the Internet.
Install Dependent ROS 1 Packages
First of all, you need to install some dependencies. These are based on Ubuntu 18.04 and ROS melodic.
$ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-joy ros-melodic-teleop-twist-joy \ ros-melodic-teleop-twist-keyboard ros-melodic-laser-proc \ ros-melodic-rgbd-launch ros-melodic-depthimage-to-laserscan \ ros-melodic-rosserial-arduino ros-melodic-rosserial-python \ ros-melodic-rosserial-server ros-melodic-rosserial-client \ ros-melodic-rosserial-msgs ros-melodic-amcl ros-melodic-map-server \ ros-melodic-move-base ros-melodic-urdf ros-melodic-xacro \ ros-melodic-compressed-image-transport ros-melodic-rqt* \ ros-melodic-gmapping ros-melodic-navigation ros-melodic-interactive-markers
Install TurtleBot3 Packages
Install TurtleBot3 via Debian Packages.
$ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-turtlebot3-msgs $ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-turtlebot3 $ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-turtlebot3-gazebo
Install Simulation Package
The TurtleBot3 Simulation Package requires turtlebot3 and turtlebot3_msgs packages as prerequisite. Without these prerequisite packages, the Simulation cannot be launched.
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src/ $ git clone -b melodic-devel https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_simulations.git $ cd ~/catkin_ws && catkin_make
Set TurtleBot3 Model Name
Set the default TURTLEBOT3_MODEL name to your model. Enter the below command to a terminal.
In case of TurtleBot3 Burger:
$ echo "export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=burger" >> ~/.bashrc
The above line write export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=burger in .bashrc file in your home directory. So whenever you open a new terminal the “burger” is assigned to the TURTLEBOT3_MODEL variable.
Start the robot simulation
There are several predefined environments that you can run the turtle inside them. In the following, you can see an empty, sample and house world.
Empty World:
$ roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_empty_world.launch
Sample World:
$ roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_world.launch
House:
$ roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_house.launch
In case you need to build your environment, you can use gazebo building editor tools (Edit > Building Editor) to create a customer shape building.
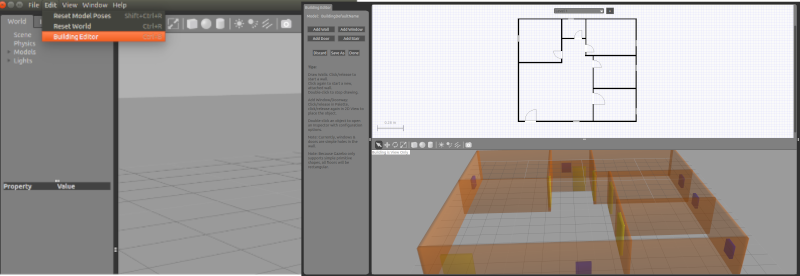
In the Gazebo Simulator, you can add simulation objects from the menu by clicking on the desired object. You'll also find tools for moving, enlarging and rotating objects in the same place.
Next we try to control the robot remotely.
Operate TurtleBot3
In order to teleoperate the TurtleBot3 with the keyboard, launch the teleoperation node with the below command in a new terminal window.
$ roslaunch turtlebot3_teleop turtlebot3_teleop_key.launch
Using the keyboard, we should now see how Turtlebot moves in the simulation.
Visualize Simulation data(RViz)
RViz visualizes published topics while the simulation is running. You can launch RViz in a new terminal window by entering the below command.
$ roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_gazebo_rviz.launch
Clearbot
Clearbot is an educational robot platform for advanced robotics enthusiasts. ClearBot opens up the opportunity to teach and learn complex technologies through simple, hands-on activities. ClearBot software is based on the ROS software framework, which provides the most up-to-date solutions for robot control, mapping, navigation, image processing, simulation, etc.
The ClearBot robot is developed for teaching purposes in cooperation with the University of Tartu Institute of Technology.
Engines
| Voltage | 12V |
| Max rpm | 500 |
| Max moment | 0.59 Nm |
| Transfer | 19: 1 |
| Encoder Resolution | 1200 cpr |
3D Camera
| Depth Resolution | 1280 x 720 |
| Min Depth | 110mm |
| Max depth | |
| Vertical field of vision | 85.2 ° |
| Horizontal field of vision | 58 ° |
| RGB camera resolution | 1920×1080 |
| RGB Camera Frame Rate | 30 fps |
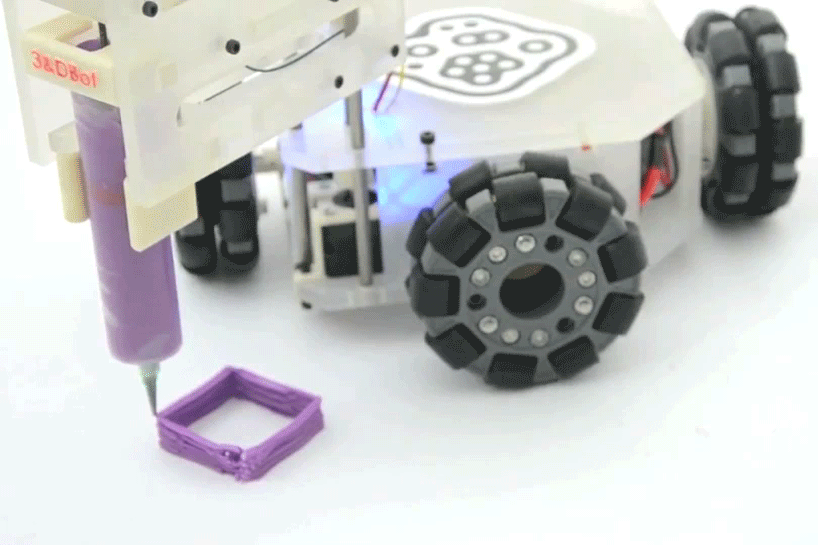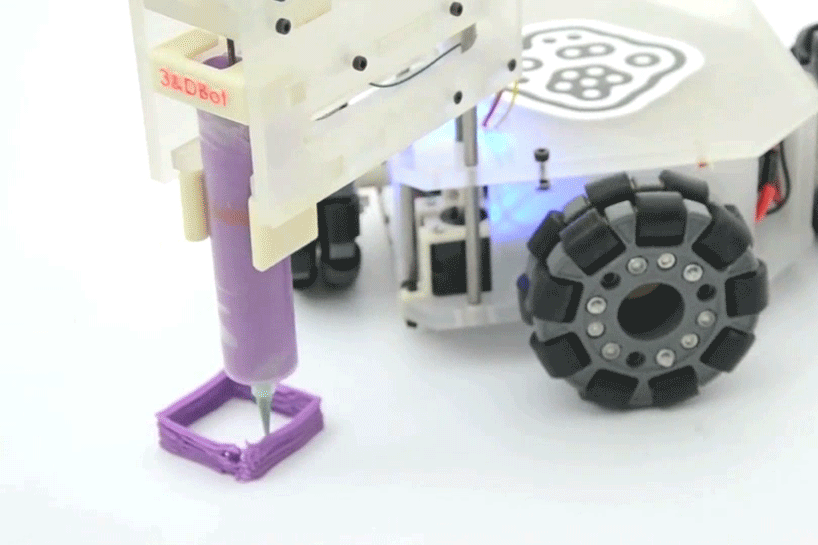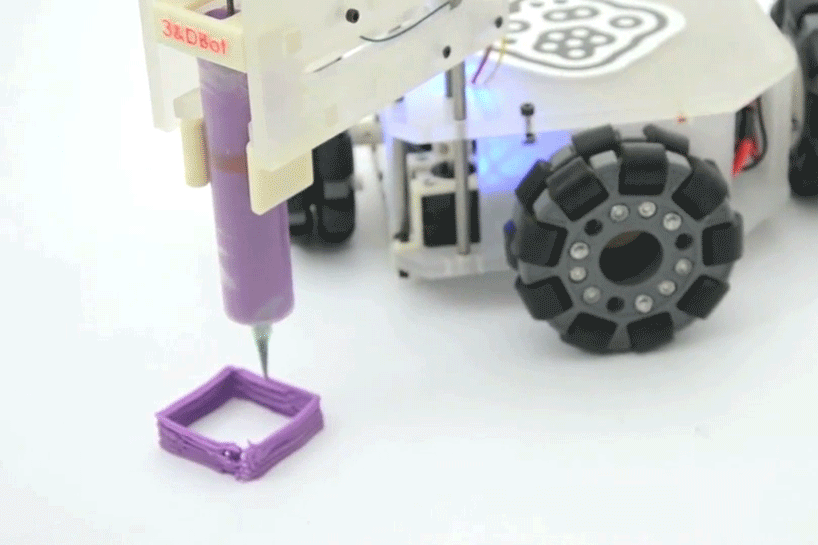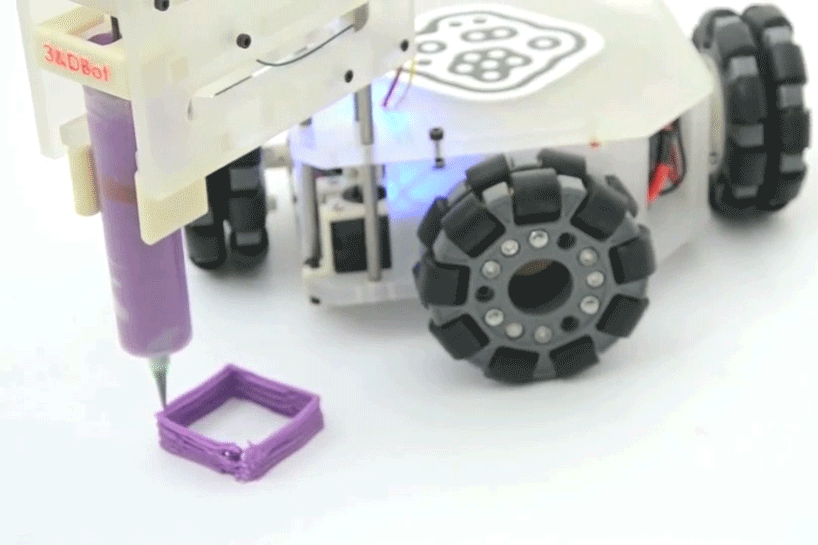
Omnir wheels
Omnidirectional wheels are wheels which are covered with rollers perpendicular to the wheel shaft, thus allowing the wheel to move in a transverse direction in addition to the normal direction of rotation. Omnidirectional wheels give the robot excellent maneuverability and flexible two-dimensional movement.